Publications
Group highlights
(For a full list of publications and patents see below or go to Google Scholar, DBLPID)
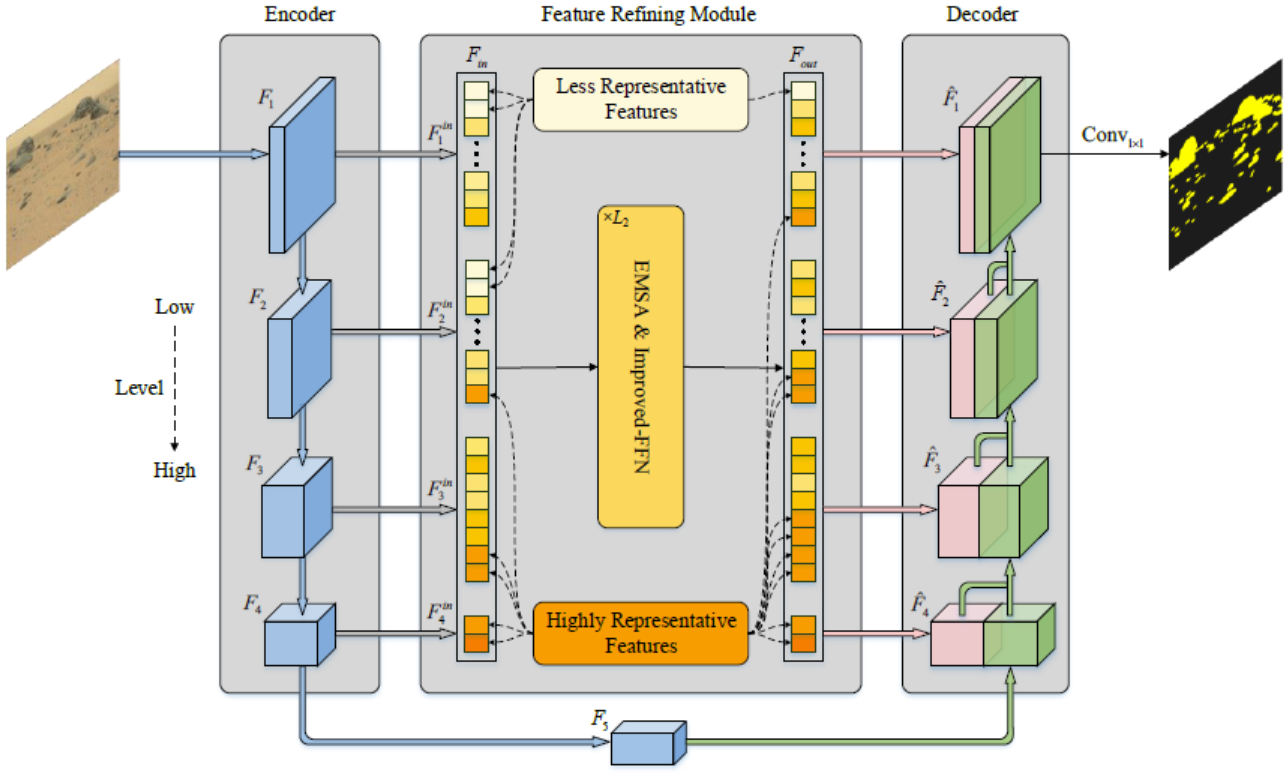
We propose RockFormer, the first U-shaped Transformer framework for Mars rock segmentation, consisting of a hierarchical encoder–decoder architecture with a feature refining module (FRM) connected between them. Specifically, the encoder hierarchically generates multiscale features using an improved vision Transformer (improved-ViT), where both abundant local information and long-range contexts are exploited. The FRM removes less representative features and captures global dependencies between multiscale features, improving RockFormer’s robustness to Martian rocks with diverse appearances. The decoder is responsible for aggregating these features for pixelwise rock prediction. For evaluation, we establish two Mars rock datasets, including both real and synthesized images. One is MarsData-V2, an extension of our previously published MarsData collected from real Mars rocks. The other is SynMars, a synthetic dataset sequentially photographed from a virtual terrain built referring to the TianWen-1 dataset. Extensive experiments on the two datasets show the superiority of RockFormer for Martian rock segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art performance with decent computational simplicity.
Haiqaing Liu, Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Yonggang Xiong
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 61, 1-16, 2023
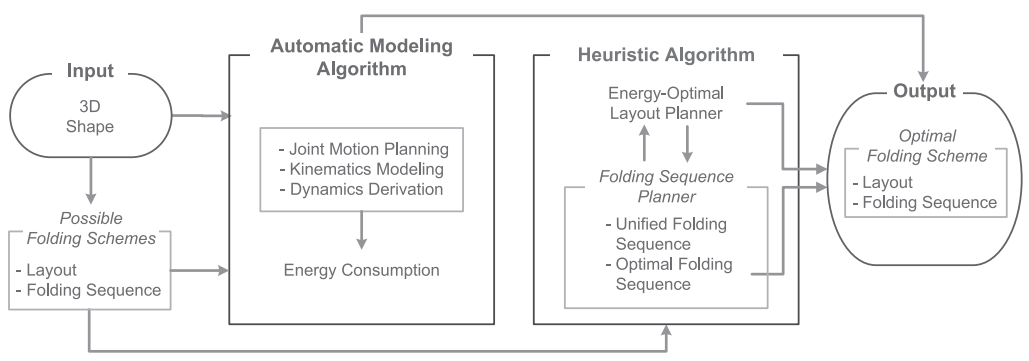
Reconfigurability in versatile systems of modular robots is achieved by changing the morphology of the overall structure as well as by connecting and disconnecting modules. Recurrent connectivity changes can cause misalignment that leads to mechanical failure of the system. This paper presents a new approach to reconfiguration, inspired by the art of origami, that eliminates connectivity changes during transformation. Our method consists of an energy-optimal reconfiguration planner that generates an initial 2D assembly pattern and an actuation sequence of the modular units, both resulting in minimum energy consumption. The algorithmic framework includes two approaches, an automatic modeling algorithm as well as a heuristic algorithm. We further demonstrate the effectiveness of our method by applying the algorithms to Mori, a modular origami robot, in simulation. Our results show that the heuristic algorithm yields reconfiguration schemes with high quality, compared with the automatic modeling algorithm, simultaneously saving a considerable amount of computational time and effort.
Meibao Yao, Christoph H Belke, Hutao Cui, Jamie Paik
The International Journal of Robotics Research 38 (1), 73-89
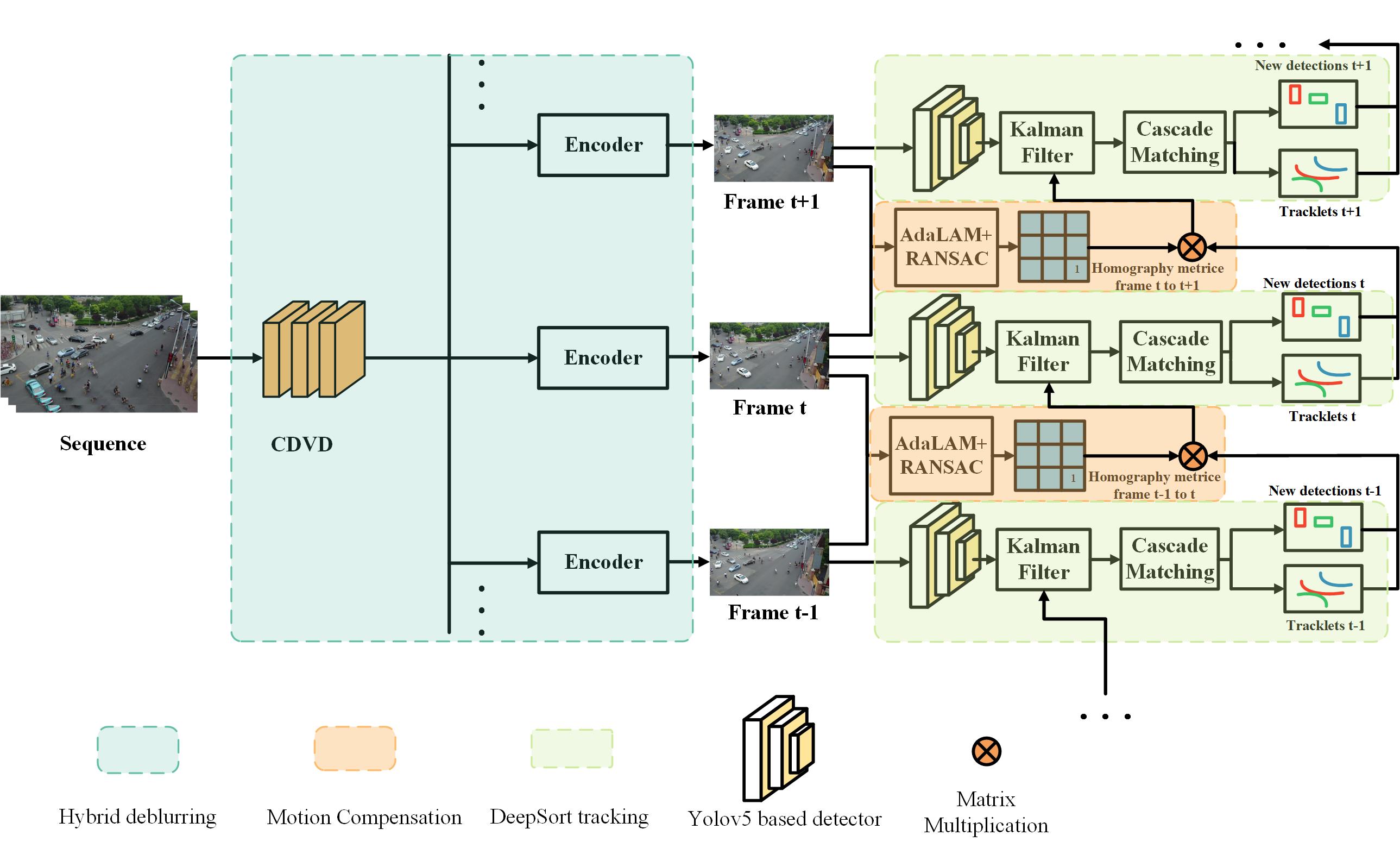
We propose a multi-object tracking framework for videos captured by UAVs, considering motion imperfection in the following two aspects: 1) motion blurring of objects due to high-speed motion of the UAV and the objects,deteriorating the performance of the detector; 2) motion coupling of the global movement of the UAV camera with the object motion, resulting in the nonlinearity of objects trajectories in adjacent frames and further more difficult to predict. For motion blurring, this paper proposes a hybrid deblurring module that deals with the blurred frames while retaining the clear frames, trading off between video tracking performance and spatio-temporal consistency. For motion coupling, we proposed a motion compensation module to align adjacent frames by feature matching, and the corrected target position is obtained in the next frame to alleviate the interference of camera movement with tracking. We evaluate the proposed methods on VisDrone dataset and validate that our framework achieves new state-of-the-art performance on UAV-based MOT systems.
Song Cheng, Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (2023), ExCel London
Modular robots hold the promise of changing their shape and even dimension to adapt to various tasks and environments. To realize this superiority, it is essential to find the appropriate morphology and its corresponding behavior simultaneously to ensure optimality of the reconfiguration. However, achieving co-optimization is challenging because robotic configuration and motion are interactive and coupled with each other, as well as their optimization processes. To this end, we proposed a co-optimization framework based on hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), consisting of a configuration model and a motion model based on the Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic policy gradient algorithm (TD3). The two network models update asynchronously with a shared reward to ensure co-optimality. We conduct simulations and experiments with the Webots platform to validate the proposed framework, and the preliminary results show that it yields high quality optimization schemes and thus allows modular robots to be more adaptive to dynamic and multi-task scenarios.
Jieqiang Sun, Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Zhibing Xie, Bo Zheng
Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), 2023, Daegu, Republic of Korea

This article presents two kernel-based rock detection methods for a Mars rover. Rock detection on planetary surfaces is particularly pivotal for planetary vehicles regarding navigation and obstacle avoidance. However, the diverse morphologies of Martian rocks, the sparsity of pixel-wise features, and engineering constraints are great challenges to current pixel-wise object detection methods, resulting in inaccurate and delayed object location and recognition. We therefore propose a region-wise rock detection framework and design two detection algorithms, kernel principle component analysis (KPCA)-based rock detection (KPRD) and kernel low-rank representation (KLRR)-based rock detection (KLRD), using hypotheses of feature and sub-spatial separability. KPRD is based on KPCA and is expert in real-time detection yet with less accurate performance. KLRD is based on KPRD with KLRR which can generate more precise rock detection results with less delay. To validate the efficiency of the proposed methods, we build a small-scale Martian rock dataset, MarsData, containing various rocks. Preliminary experimental results show that our methods are efficient in dealing with complex images containing rocks, shadows, and gravel. The code and data are available at: https://github.com/CVIR-Lab/MarsData.
Xueming Xiao, Meibao Yao, Haiqiang Liu, Jiake Wang, Lei Zhang, Yuegang Fu
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021

We propose a novel auto rock detection scheme via sparse based background modeling for planetary rover. Instead of pixel level image processing and pre training, we deal with the detection issue by region contrast enhancement. Our method consists of a rough detection algorithm to auto-label conservative background regions and a background modeling algorithm to precisely detect rocks. Background is reconstructed in feature space with the labeled regions as dictionary via sparse representation. Contrast map is enhanced by the error of original image and reconstructed background. Afterwards, rock is directly segmented by an auto threshold.
Xueming Xiao, Hutao Cui, Meibao Yao, Yuegang Fu, Wanqiang Qi
IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, 2018
Patents
XXk
XXX
XX/XX (2020)
Full List of publications
RockFormer: A U-Shaped Transformer Network for Martian Rock Segmentation
Haiqaing Liu, Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Yonggang Xiong
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 61, 1-16, 2023
A reconfiguration strategy for modular robots using origami folding
Meibao Yao, Christoph H Belke, Hutao Cui, Jamie Paik
The International Journal of Robotics Research 38 (1), 73-89
DC-MOT: Motion Deblurring and Compensation for Multi-Object Tracking in UAV Videos
Song Cheng, Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (2023), ExCel London
Co-optimization of Morphology and Behavior of Modular Robots via Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jieqiang Sun, Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Zhibing Xie, Bo Zheng
Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), 2023, Daegu, Republic of Korea
A fast terminal sliding mode control scheme with time-varying sliding mode surfaces
Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Yang Tian, Hutao Cui
Journal of the Franklin Institute,358,10 (2021)
A Kernel-Based Multi-Featured Rock Modeling and Detection Framework for a Mars Rover
Xueming Xiao, Meibao Yao, Haiqiang Liu, Jiake Wang, Lei Zhang, Yuegang Fu
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021
A hybrid wavelength selection strategy-based quantitative analysis model for LIBS data from standard ground samples of the Curiosity rover on Mars
Yan Yu, Meibao Yao, Jipeng Huang
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2022, 37(11), 2362-2376
A two-time scale control scheme for on-orbit manipulation of large flexible module
Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Yang Tian, Hutao Cui
Acta Astronautica 154, (2019)
Optimal distribution of active modules in reconfiguration planning of modular robots
Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Christoph H Belke, Hutao Cui, Jamie Paik
Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics,11,1 (2019)
An Actuation Fault Tolerance Approach to Reconfiguration Planning of Modular Self-folding Robots
Meibao Yao, Xueming Xiao, Yang Tian, Hutao Cui, Jamie Paik
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), (2020)
Svrat: A Skeleton-Based Intelligent Monitoring System for Violence Recognition and Abuser Tracking
Haiqiang Liu, Meibao Yao, Linlin Wang
2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), 1-6
Towards peak torque minimization for modular self-folding robots
Meibao Yao, Hutao Cui, Xueming Xiao, Christoph H Belke, Jamie Paik
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), (2018)
An Adaptive Backstepping-Based Controller for Trajectory Tracking of Wheeled Robots
Song Cheng, Haoming Liu, Meibao Yao
2021 4th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), 539-544
Safe Mars landing strategy: Towards lidar-based high altitude hazard detection
Xueming Xiao, Meibao Yao, Hutao Cui, Yuegang Fu
Advances in Space Research 63, 8 (2019)
Crater edge-based flexible autonomous navigation for planetary landing
Yang Tian, Meng Yu, Meibao Yao, Xiangyu Huang
The Journal of Navigation 72 (3), 649-668
Autonomous rock detection on mars through region contrast
Xueming Xiao, Hutao Cui, Meibao Yao, Yang Tian
Advances in Space Research 60, 3 (2017)
Auto rock detection via sparse-based background modeling for mars rover
Xueming Xiao, Hutao Cui, Meibao Yao, Yuegang Fu, Wanqiang Qi
IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, 2018
The Premise of Automatic Four-wheel Alignment: Intelligent Identification and Processing of Rim Targets
Yifan Wang, Meibao Yao
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2203 (1), 012007
A Configuration Design Method for Reconfigurable Robots Based on Terrain Understanding
Hua Shang, Yurong Xi, Zhibing Xie, Xueming Xiao, Meibao Yao
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2203 (1), 012023